After 1 Year, Weekly Doses of Dupilumab Most Effective at Managing Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Research By: Margaret Collins, MD | Marc Rothenberg, MD, PhD
Post Date: August 31, 2023 | Publish Date: Aug. 31, 2023
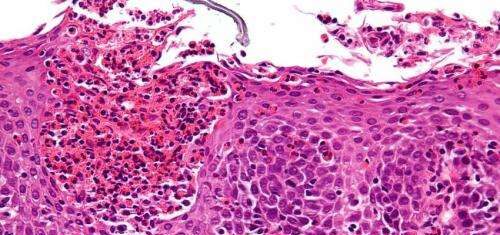
After one year of follow-up, a 65-center, 10-nation clinical study reinforces earlier findings that weekly dupilumab treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) produces stronger histologic, symptomatic, endoscopic, and molecular improvements compared to treatment every two weeks.
Results from the study, led by Cincinnati Children’s physician–scientist Marc Rothenberg, MD, PhD, and co-authored by Margaret Collins, MD, Division of Pathology, were published online Aug. 31, 2023, in The Lancet: Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Dupilumab is a biologic that blocks the shared receptor component for interleukin 4 and interleukin 13, two cytokines known to be involved in pathogenesis of EoE. More information about this double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study can be found at ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT03633617
In addition to this study, the cover of the journal’s September print edition focuses on another research study led by Rothenberg and colleagues. Those findings, published online in June, report that the monoclonal antibody benralizumab successfully reduces eosinophil cell counts but does not improve the symptoms nor biomarker results for eosinophilic gastritis (EoG).
Read More: Wider Search Needed to Better Treat Eosinophilic Food Allergy
| Original title: | Efficacy and safety of dupilumab up to 52 weeks in adults and adolescents with eosinophilic oesophagitis (LIBERTY EoE TREET study): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial |
| Published in: | The Lancet: Gastroenterology and Hepatology |
| Publish date: | Aug. 31, 2023 |
Research By


The Rothenberg CURED Research Laboratory, supported by the Campaign Urging Research for Eosinophilic Diseases (CURED), is focused on elucidating the mechanisms of allergic responses, especially in mucosal tissues such as the gastrointestinal tract and lung.







