Absence Epilepsy Study Group Provides Dosing Guidance for Ethosuximide
Research By: Kana Mizuno, PhD | Tracy Glauser, MD
Post Date: June 14, 2023 | Publish Date: June 14, 2023
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology | Top Scientific Achievement

In 2012, research led by Tracy Glauser, MD, and colleagues with the Childhood Absence Epilepsy Study Group identified the anticonvulsant medication ethosuximide as the optimal option for new-onset childhood absence epilepsy rather than lamotrigine and valproic acid. A decade later, a new study from the group, also led by Glauser, provides important precision dosing recommendations aimed at reducing a significant rate of seizures continuing after initial monotherapy.
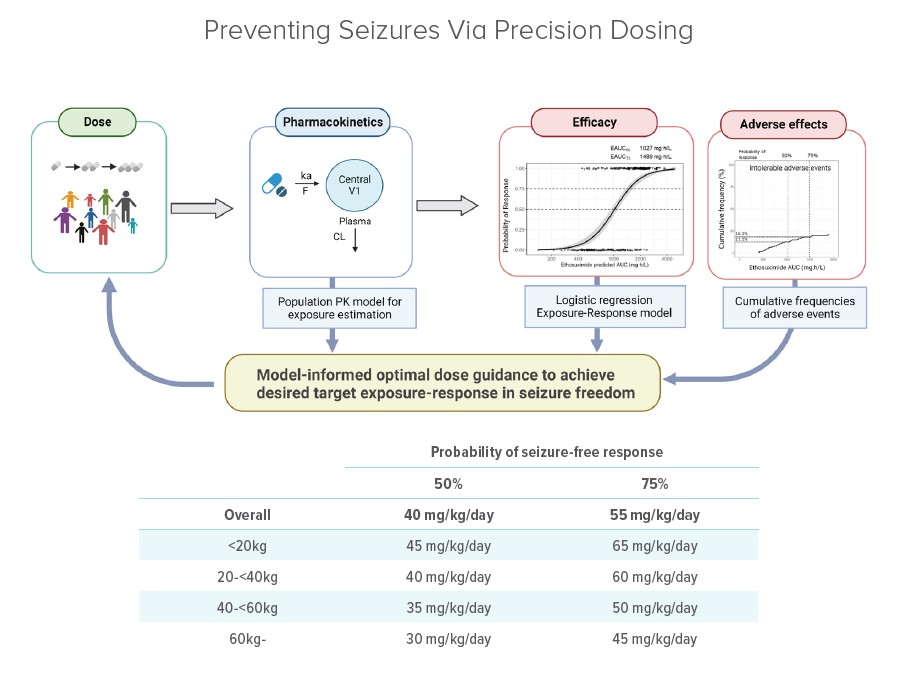
The clinical trial involved building quantitative pharmacology models to describe pharmacokinetics and exposure-seizure-free response to inform precision dosing for initial ethosuximide monotherapy. Plasma concentration data were collected from 211 total participants. Dose titration occurred over a 16–20-week period until patients experienced seizure freedom or intolerable side effects. Based on an initial monotherapy cohort of 103 participants, 84 achieved seizure freedom within a wide range of ethosuximide exposure, shown as area under the curves (AUC).
Overall, AUC estimates to reach seizure freedom ranged from 420 to 2,420 micrograms per milliliter per hour (μg·h/ mL). The team found that when the AUC reached 1,027 μg·h/ mL, patients had a 50% probability of seizure freedom, while 1,489 μg·h/mL produced a 75% probability. The corresponding frequency of intolerable adverse events was 11% and 16%, respectively.
The co-authors report that achieving the targeted exposure levels requires a daily dose of 40 mg/kg to achieve a 50% probability of seizure freedom, while 55 mg/kg offers a 75% probability.
“This model-informed guidance suggests that many/ some/most patients receiving ethosuximide as a monotherapy but not achieving seizure freedom may have been under-dosed at treatment onset,” Glauser says. “Employing this new model offers the potential to optimize therapy success for children with absence epilepsy.”
Co-authors included Cincinnati Children’s experts Alexander Vinks, PharmD, PhD, Min Dong, PhD, Tsuyoshi Fukuda, PhD, Peggy Clark, MSN, APRN, PNP, and Kana Mizuno, PhD (first author). Colleagues also contributed from Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, University of California San Diego, Rainbow Babies and Children’s Hospital in Cleveland, Montefiore Medical Center in New York, and Children’s National Health System in Washington, DC.
More 2023 Research Highlights
Chosen by the Division of Translational and Clinical Pharmacology
Tang Girdwood S, Hasson D, Caldwell JT, et al. Relationship between piperacillin concentrations, clinical factors and piperacillin/tazobactam-associated acute kidney injury. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023;78(2):478-487. doi:10.1093/jac/dkac416
Poweleit EA, Vinks AA, Mizuno T. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Approaches to Facilitate Therapeutic Drug Management and Model-Informed Precision Dosing. Ther Drug Monit. 2023;45(2):143-150. doi:10.1097/FTD.0000000000001078
Alghamdi A, Seay S, Hooper DK, et al. Tacrolimus pharmacokinetics are influenced by CYP3A5, age, and concomitant fluconazole in pediatric kidney transplant patients. Clin Transl Sci. 2023;16(10):1768-1778. doi:10.1111/cts.13571
Tang Girdwood S, Tang P, Fenchel M, et al. Pharmacokinetic parameters over time during sepsis and the association of target attainment and outcomes in critically ill children and young adults receiving ceftriaxone. Pharmacotherapy. 2023;43(7):609-621. doi:10.1002/phar.2774
Dong M, Ware RE, Dallmann A, Vinks AA. Hydroxyurea treatment for sickle cell anemia during pregnancy and lactation: Current evidence and knowledge gaps. Pharmacotherapy. 2023;43(5):419-429. doi:10.1002/phar.2793
View more discoveries from 50 research divisions and areas
Return to the 2023 Research Annual Report main features
| Original title: | Model-Informed Precision Dosing Guidance of Ethosuximide Developed from a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial of Childhood Absence Epilepsy |
| Published in: | Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics |
| Publish date: | June 14, 2023 |
Research By


An expert in neurology, clinical pharmacology and genomics, Dr. Glauser’s research focuses on clinical pharmacology, pharmacogenetics and antiepileptic clinical trials.