Stem Cell Rejuvenation Technology Licensed to Mogling Bio
Research By: Yi Zheng, PhD
Post Date: September 13, 2023 | Publish Date:
Nearly two decades of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) research and discovery culminated in an important milestone this year. Mogling Bio Inc., a privately owned, preclinical stage biopharmaceutical company, entered into a global exclusive agreement with Cincinnati Children’s for continued development of CDC42 inhibitors to rejuvenate aged HSCs.
By enhancing the body’s access to revitalized stem cells, this innovation has the potential to revolutionize immune system recovery after cancer therapies, enhance the efficacy of therapeutic agents, increase transplantation success rates and offer comprehensive therapy for individuals with compromised blood systems.
Yi Zheng, PhD, director of Experimental Hematology and Cancer Biology, executive co-director of the Cancer and Blood Diseases Institute and the Marjory Johnson Endowed Chair of Drug Discovery, dedicated years to studying the CDC42 signaling mechanism and devising small molecule CDC42 inhibitors.
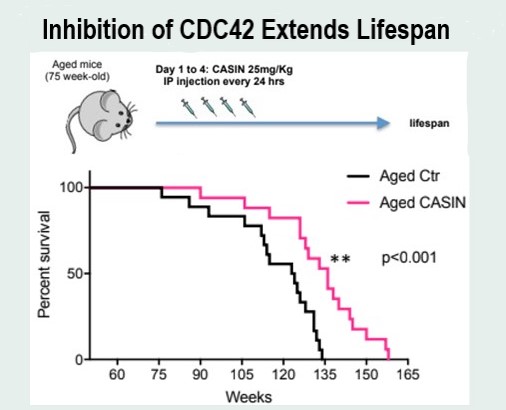
This journey began in 2006, when Zheng discovered that gene targeting CDC42 in mouse models and application of CASIN, a naturally occurring CDC42 inhibitor, could effectively open the bone marrow niche, enabling stem cells to enter the blood stream. This breakthrough held potential implications for gene therapies targeting genetic blood disorders like sickle cell disease and paved the way for research on therapeutics that rejuvenate aged HSCs. As research progressed, Zheng and his colleagues went on to publish more research exploring the CD42 signaling mechanism. Among them articles in Cell Stem Cell, Nature, Experimental Cell Research, Leukemia and Aging Cell.
“CDC42 inhibitors like CASIN have shown astonishing preclinical results,” said Jüergen Reess, MD, Mogling Bio’s CEO. “This agreement will help us in our goal to translate these findings into treatment options for patients in need.”
The potential applications of this technology are vast and could impact patients in several key areas:
- Speeding up blood and immune system recovery after cancer therapies: By revitalizing aged HSCs of older adult patients, this technology can facilitate the restoration of the blood and immune systems, which often become compromised in older patients.
- Enhancing the effectiveness of therapeutic agents: The release of leukemia-initiating cells from the bone marrow increases their susceptibility to chemotherapeutic agents, potentially improving treatment outcomes for leukemia patients.
- Increasing the rate of transplantation success: By administering CASIN, there was effective opening of bone marrow niche, allowing for improved engraftment of the donor stem cells. This suggests that this technology can enhance the success of transplantation procedures.
- Providing comprehensive therapy for immunocompromised patients: By optimizing HSC mobilization and engraftment, this technology holds promise as a holistic therapeutic approach for individuals with compromised immune systems.
This groundbreaking technology developed at Cincinnati Children’s presents a promising solution to the challenges surrounding hematopoietic stem cell mobilization and engraftment, as well as rejuvenation. With its ability to revolutionize blood and immune system recovery, amplify the effectiveness of therapeutic agents, increase transplantation success, and provide comprehensive therapy for individuals with compromised immune systems, this breakthrough has the potential to transform many areas of medical treatment.
Research By

My lab focuses on studies of the physiological and pathological function and the mechanism of regulation of Rho family GTP-binding proteins.