Science Watchers Hail Discoveries From Experts at Cincinnati Children’s
Post Date: December 17, 2019 | Publish Date:
Three studies authored or co-authored by scientists at Cincinnati Children’s have been ranked among the top discoveries of 2019 by noted science journals, tracking services and communicators.
These studies and several others involving Cincinnati Children’s investigators have been widely shared among scientists, the news media and others who focus on child health.
Mitochondrial DNA Finding Surprises Many
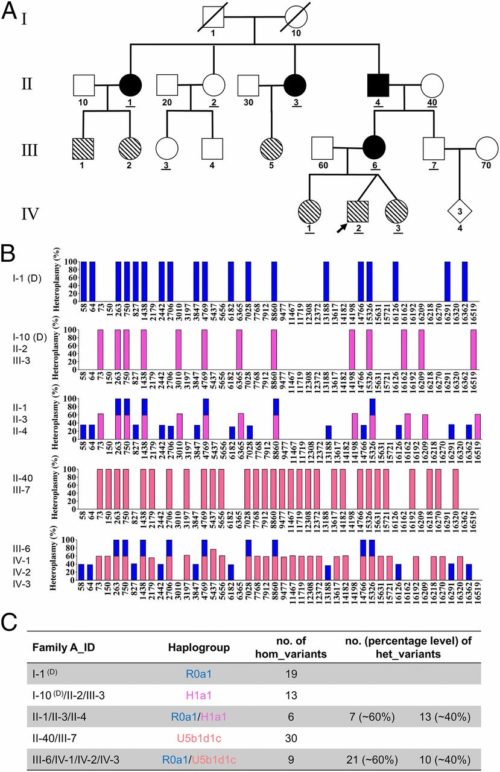
Nature, which publishes several highly respected academic journals, recently posted a list of “10 Remarkable Papers from 2019.” That list includes a study published in PNAS, led by Shiyu Luo, PhD, and Taosheng Huang, MD, PhD, Division of Human Genetics at Cincinnati Children’s.
This study rocked the science world by providing powerful evidence that, in rare cases, fathers can pass mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) to their children. Until this finding, all mtDNA was thought to be passed along solely by mothers.
Read the Nature story: Mitochondrial DNA can be inherited from fathers, not just mothers
Huang’s paternal mitochondrial DNA paper also was ranked No. 69 among the 100 most-shared discoveries of 2019, as tracked by Altmetric, which culled its list from 2.7 million research outputs published in the past year.
Huang’s paper received an Altmetric score of 2645. This score reflects 61 news stories, 4,100 tweets reaching nearly 7 million followers, plus mentions detected in blogs, Facebook, online videos and other sources.
Another highly-shared study, published in The Lancet, was ranked No. 92 with an Altmetric score of 2390. Jessica Kahn, MD, MPH, Division of Adolescent and Transition Medicine, was a member of the HPV Vaccination Impact Study Group that provided data and supplementary analyses for the project.
Cardiac Stem Cell Study Challenges Dogma
In addition to these kudos, the medical social media influencer Eric Topol, MD, (182,000+ followers on Twitter) listed two Cincinnati Children’s papers among his top choices for 2019:
My favorite papers challenge biomedical dogma. Here's my summary of the ones in 2019 that provided evidentiary shakeups (2nd annual list)
[let me know the ones I missed] pic.twitter.com/AmBmXZq5ug— Eric Topol (@EricTopol) December 14, 2019
One of Topol’s choices was Huang’s paternal mitochondrial DNA paper. The other was a finding recently published by Jeffery Molkentin, PhD, Executive Co-Director at our Heart Institute.
In 2014, Molkentin raised questions about the validity of experiments using cardiac stem cell injections to help people grow new heart muscle after surviving heart attacks. The stem cells failed to generate new heart muscle. He followed up that work with a study published Nov. 27, 2019, in Nature that further explains what occurs.
Molkentin’s new study reports that instead of prompting new muscle cell growth, cardiac stem cells—be they dead or alive—prompt an immune response that produces a more optimized scar and improved contractile properties.
Rethinking Antibiotic Usage Levels Continues
Cincinnati Children’s expertise also was reflected in a “Best of 2019” list from the journal Pediatrics.
The list includes a study published in September 2019 that demonstrated the effectiveness of short-term antibiotic courses for treating infant urinary tract infections. The study was co-authored by Samir Shah, MD, Director of our Division of Hospital Medicine. The findings reflect another step in ongoing efforts to reduce antibiotic overuse.
More highly-shared studies from 2019 that involved Cincinnati Children’s scientists
Associations Between Screen-Based Media Use and Brain White Matter Integrity in…
Maternal and fetal genetic effects on birth weight and their relevance to…
Modelling human hepato-biliary-pancreatic organogenesis from the foregut–midgut…
In utero gene editing for monogenic lung disease
Hydroxyurea for Children with Sickle Cell Anemia in Sub-Saharan Africa





