Novel Cardiac Stent Designed to be Expanded as Young Patients’ Arteries Grow
Post Date: May 2, 2022 | Publish Date:
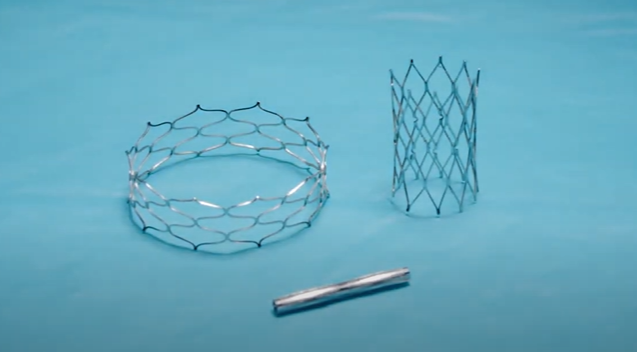
Feasibility study underway for vascular device that could eliminate the need for multiple replacement surgeries
Cincinnati Children’s has become the second medical center to implant a new minimally invasive cardiac stent specifically designed to expand as younger patients grow, reducing the need for repeated risky and expensive open-heart surgeries to replace stents that have become too small.
Patients born with congenital heart disease, such as a narrowing of the aorta or pulmonary arteries, often require mesh tubes called stents to help keep their arteries open and blood flowing. But pediatric stents present challenges not found in adults–namely that adults will not outgrow their stents. With young children, and infants in particular, stents become ineffective as their arteries grow, requiring them to be replaced at multiple points during their lives.
The Renata Minima stent, which was first implanted in a Cincinnati Children’s patient in March 2022 as part of an early feasibility study, is initially installed at about the diameter of a drinking straw via a balloon catheter procedure. It can be expanded up to about the diameter of a nickel to keep pace with a child’s growth – all with minimally invasive procedures rather than open-chest surgeries.
“This stent is a significant advance for children with heart disease because it is the first purpose-built stent for children,” says Shawn Batlivala, MD, a pediatric cardiologist at Cincinnati Children’s. “In children, especially young children, we cannot implant a stent at adult size, so it is necessary to either remove stents via surgery or perform a more difficult procedure involving fracturing of stents when the child has outgrown them. The Renata stent was built to be implanted at a small size and can be expanded to adult size over time while maintaining its strength.”
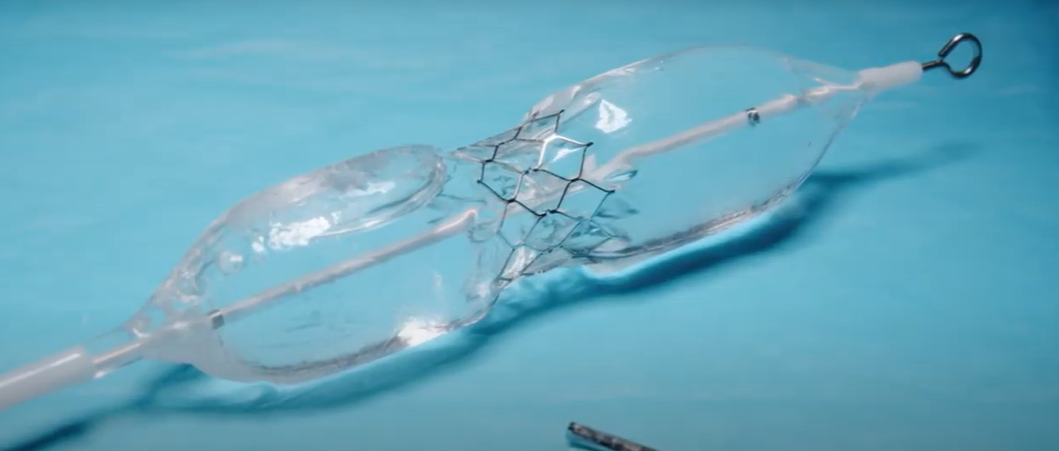

The first patient at Cincinnati Children’s to receive the stent was an 18-month-old girl named Kendra who had it implanted in her pulmonary artery. Previously, Kendra would have received a non-pediatric stent. But because Cincinnati Children’s is one of the few sites in the United States enrolled in this feasibility study, she was able to receive the Renata stent and potentially forgo future procedures.
Cincinnati Children’s was the first site in the Midwest to implant this new stent, and first outside of the primary site in Los Angeles. Of the 10 stents implanted as part of the study, four were done at Cincinnati Children’s. The medical center also will participate in the next phase of the FDA approval process, which will involve enrolling additional patients and following them for a longer period of time.
“Cincinnati Children’s is a world-leader in innovation for pediatric conditions,” Shabana Shahanavaz, MBBS, director of the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory at Cincinnati Children’s, says. “Our cath lab strives to be at the forefront of advancements for children with heart disease. The Renata stent is a prime example of how we are involved in leading our field forward – by partnering with leaders and academics in the industry to improve the lives of our patients.”