Immune System Works Differently Between and First and Later Pregnancies
Research By: Sing Sing Way, MD, PhD
Post Date: June 23, 2020 | Publish Date: June 23, 2020
Study provides biological insights into miscarriage and preterm birth
Among the holy quests of serious and mysterious medical challenges that doctors and research scientists strive to vanquish is preventing miscarriages, stillbirth and other pregnancy complications including preterm births.
“We don’t understand at a cellular and molecular level what causes miscarriages or preterm births, mainly because we don’t know how pregnancy works normally,” says Sing Sing Way, MD, PhD, Director of the Center for Inflammation and Tolerance at Cincinnati Children’s.
Way and his colleagues are part of a small army of scientists, physicians and others looking for answers to these basic questions with enormous health and scientific implications. Their goal is to devise improved therapies to stem the tide of what remains a severe and entrenched public health crisis.
Way’s research focuses on how the immune system changes during pregnancy, and immunological perturbations associated with pregnancy complications. The scientists use animal pregnancy models so that variables in evaluating differences in human pregnancy outcomes including maternal age, genetic diversity between parents and number of prior pregnancies can be properly evaluated.
A mother’s immune system is altered during pregnancy to prevent a fetus from being rejected by the body. It is a delicate immunological balance that, if disrupted, could cause a miscarriage or multiple miscarriages. And unfortunately, that balance too often becomes disrupted by environmental exposures or physiological changes leading to pregnancy complications.
New understanding of pregnancy
Way’s team is now adding an important new wrinkle by reporting in Cell Reports that a woman’s immune system behaves very differently between a first and second pregnancy.
Researchers say this could lead to better, more personalized ways to protect pregnancies.
“First and subsequent pregnancies work very differently and understanding these differences can lead to improved therapies that target the unique immunological perturbations that occur in first and later pregnancies,” explained Way, the study’s principal investigator.
Diverging pathways
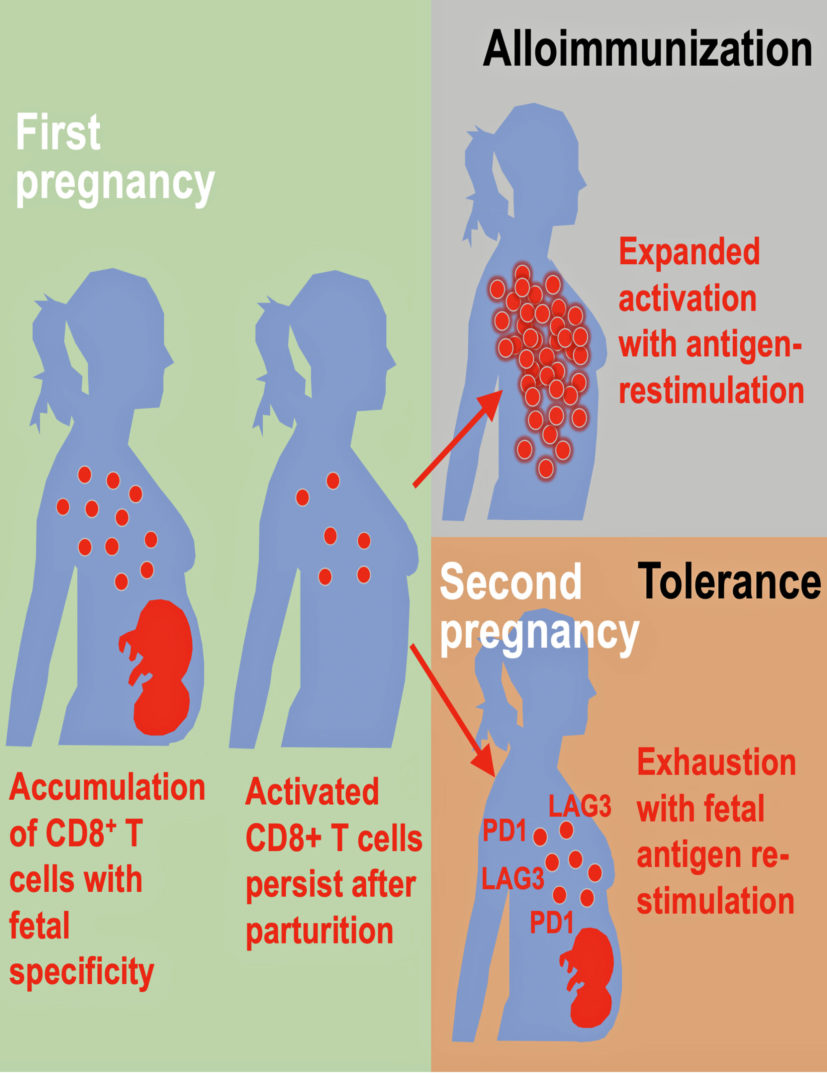
The study shows the immune pathways that promote a healthy first pregnancy are not the same pathways that promote later pregnancies.
The authors discuss how pregnancy causes physiological exposure, and often re-exposure, to foreign fetal allo-antigens, which are expressed by the developing fetus. These allo-antigens interact directly with the mother’s immune system. The consequences after pregnancy are highly varied, they note.
The researchers found evidence of both alloimmunization (where the immune system attacks) and expanded tolerance phenotypes where it does not. Their data show that pregnancy primes accumulation of fetal-specific maternal CD8+ T cells, and that mothers remember their babies immunologically in that these cells persists as an activated memory pool after she gives birth.
Expression to two proteins, PD-1 and LAG-3 by what are called memory T cells, reminds the cells to again be tolerant of the developing fetus again during subsequent pregnancies. But molecular disruptions that neutralize expression of these proteins unleash the activation of fetal-specific CD8+ T cells, causing miscarriage selectively during subsequent, but not first pregnancies, according to the study’s first author, Jeremy Kinder, a research associate on Way’s laboratory team.
About the study
Funding support for the study came in part from the National Institutes of Health (R01AI120202, R01AI124657 and DP1AI131080); the HHMI Faculty Scholar’s program , the March of Dimes Ohio Collaborative for Prematurity Research, and a Burroughs Wellcome Fund Investigator in the Pathogenesis Award.
— Post written by Nick Miller
| Original title: | CD8+ T cell functional exhaustion overrides pregnancy induced fetal antigen alloimmununization |
| Published in: | Cell Reports |
| Publish date: | June 23, 2020 |
Research By