How CHD8 Mutations Contribute to Autism Spectrum Disorders
Research By: Qing Richard Lu, PhD
Post Date: June 30, 2019 | Publish Date: June 18, 2018
Scientists here have clarified how mutations in the gene CHD8 harm the brain and contribute to autism spectrum disorders. They reported their findings June 18, 2018, in Developmental Cell.
Previous studies had linked CHD8 mutations to autism and abnormalities in the brain’s white matter, but the underlying biology has been a mystery.
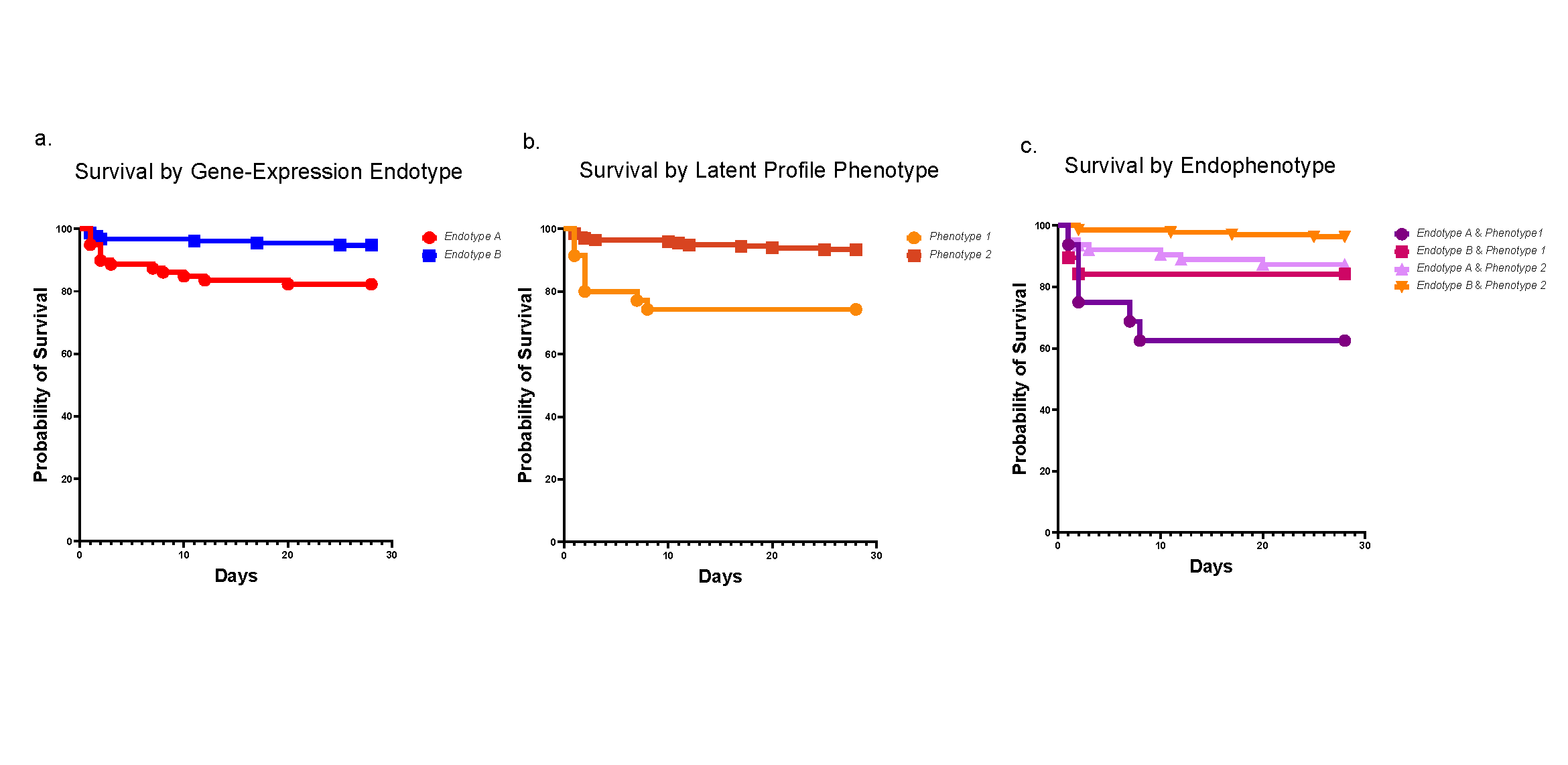
This study showed that disruption of CHD8 hinders production and maintenance of nerve insulation, harming the brain’s neuronal connections and contributing to white matter damage. Mice engineered to lack CHD8 protein in the oligodendrocytes—cells that produce the protective nerve sheath—exhibited behavioral anomalies and seizures, according to lead investigator Q. Richard Lu, PhD, Division of Experimental Hematology and Cancer Biology.
Although study results are early, Lu says the work could lead to treatments that restore function to faulty CHD8-dependent processes.
| Original title: | Dual Requirement of CHD8 for Chromatin Landscape Establishment and Histone Methyltransferase Recruitment to Promote CNS Myelination and Repair |
| Published in: | Developmental Cell |
| Publish date: | June 18, 2018 |
Research By